Health Library
Ringworm of the body
Tinea corporis; Fungal infection - body; Tinea circinata; Ringworm - body
Ringworm is a skin infection that is caused by fungi. It is also called tinea.
Related skin fungus infections may appear:
- On the scalp
- In a man's beard
- In the groin (jock itch)
- Between the toes (athlete's foot)
Images





I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Fungi are germs that can live on the dead tissue of the hair, nails, and outer skin layers. Ringworm of the body is caused by mold-like fungi called dermatophytes.
Ringworm of the body is common in children, but can occur in people of all ages.
Fungi thrive in warm, moist areas. A ringworm infection is more likely if you:
- Have wet skin for a long time (such as from sweating)
- Have minor skin and nail injuries
- Do not bathe or wash your hair often
- Have close contact with other people (such as in sports like wrestling)
Ringworm can spread quickly. You can catch it if you come into direct contact with an area of ringworm on someone's body. You can also get it by touching items that have the fungi on them, such as:
- Clothing
- Combs
- Pool surfaces
- Shower floors and walls
Pets can also spread ringworm. Cats are common carriers.
Symptoms
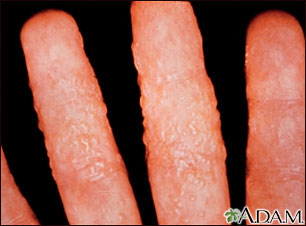
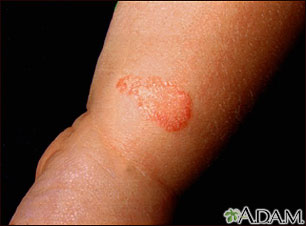
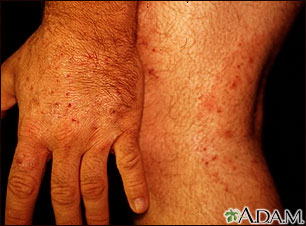
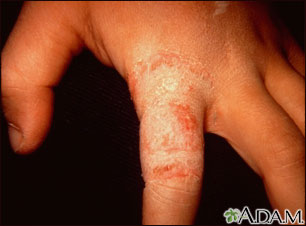
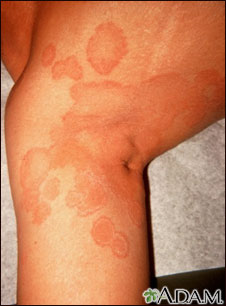
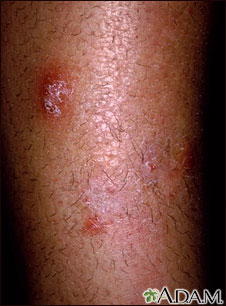
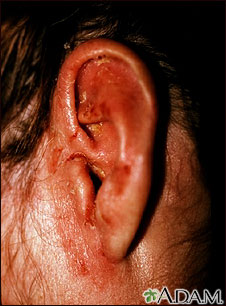
The rash begins as a small area of red, raised spots and pimples. The rash slowly becomes ring-shaped, with a red, raised border and a clear center. The border may look scaly.
The rash may occur on the arms, legs, face, or other exposed body areas.
The area may be itchy.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can often diagnose ringworm by looking at your skin.
You may also need the following tests:
- Examination of a skin scraping from the rash under a microscope using a special test
- Skin culture for fungus
- Skin biopsy
Treatment
Keep your skin clean and dry.
Use creams that treat fungal infections.
- Creams that contain miconazole, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, terbinafine, or oxiconazole, or other antifungal medicines, are often useful in controlling ringworm.
- You can buy some of these creams over-the-counter, or your provider may give you a prescription.
To use this medicine:
- Wash and dry the area first.
- Apply the cream, beginning just outside the area of the rash and moving toward the center. Be sure to wash and dry your hands afterward.
- Use the cream twice a day for 7 to 10 days.
- Do not use a bandage over ringworm.
Your provider may prescribe medicine to take by mouth if your infection is very bad.
A child with ringworm can return to school once treatment has started.
To prevent the infection from spreading:
- Wash clothing, towels, and bedding in hot, soapy water and then dry them using the hottest heat recommended on the care label.
- Use a new towel and washcloth every time you wash.
- Clean sinks, bathtubs, and bathroom floors well after each use.
- Wear clean clothes every day and do not share clothes.
- If you play contact sports, shower right away afterward.
Infected pets should also be treated. This is because ringworm can spread from animals to humans by contact.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Ringworm often goes away within 4 weeks when using antifungal creams. The infection may spread to the feet, scalp, groin, or nails.
Possible Complications
Two complications of ringworm are:
- Skin infection from scratching too much
- Other skin disorders that require further treatment
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if ringworm does not get better with self-care.
Related Information
RingwormRingworm of the scalp
Jock itch
Athlete's foot
Cellulitis
References
Dinulos JGH. Superficial fungal infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 13.
Hay RJ. Dermatophytosis (ringworm) and other superficial mycoses. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 266.
Patterson JW. Mycoses and algal infections. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2021:chap 26.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 11/18/2022
Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
 | A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
